Django project
Tips for navigating the slides:
- Press O or Escape for overview mode.
- Visit this link for a nice printable version
- Press the copy icon on the upper right of code blocks to copy the code
Class outline:
- Review
- Getting external data in Django
- Django template variables
- Charts with Plotly
- Wrap-up
Review: Frameworks
What's a framework?
Software frameworks are packages of starter code that you can build on. They're often used to develop web applications quickly. Frameworks do things like:
- Provide code for common pieces of functionality, like serving web pages and authenticating users
- Help you follow security best practices without having to be a web security expert
- Allow you to focus on building functionality that's unique to your app
Python web app frameworks
There are many Python frameworks out there! The 2 most popular general-purpose frameworks for web applications are:
Both allow you to build web applications and/or APIs, and both have a robust extension ecosystem
Django features
In this class, we'll use Django. Its features include:
- Built-in web server for development and testing
- Functionality for processing HTTP requests with custom logic
- Template system for displaying dynamic web pages to users
- Database connectivity + built-in methods for reading/writing
- Data modeling functionality to support converting between database data and Python objects
- Built-in admin interface + authentication features
- And much more! See feature overview
Ways to use Django
- All-in-one MVT (model-view-template) app, which means that both the app logic and the HTML page construction happen on the server side, within Django. This doesn't allow page content to change after loading, unless you add Javascript over the top.
- REST API backend only that performs app logic and returns JSON to a separate frontend app (ex, a Javascript framework like React or Angular). This is a more "modern" approach that allows content to change after page load.
In this class, we'll use the MVT approach
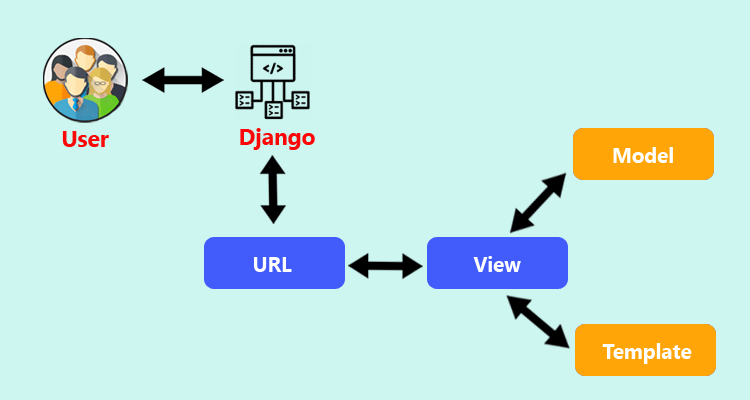
Django MVT
- Model The data access layer. This layer contains everything about the data: how to access it, how to validate it, which behaviors it has, and the relationships between the data. Note that this layer is not required! Sometimes a request only generates a view, which populates a template.
- View The logic layer. This layer contains the logic that accesses the model and populates the appropriate template.
- Template The presentation layer. This layer defines how something should be displayed on a Web page .
Django MVT
Installing Django locally
- Django is available in PyPi and can be installed with
pip install, like any other package. - When you install Django, you're downloading the source code which is maintained in Github
- After installing Django, the first step is to create a new project
Django in Replit
For our project, we'll run Django in Replit. From here on out, we'll follow this tutorial:
Python 2 Django tutorial
The tutorial will guide us through building a simple Django web app the displays the current weather based on the user's location.
Homework review
- Basic Django setup tutorial steps 1-3!
- Repl example with completed Django setup: Python2WeatherAppStart
(Note: If you fork this Replit, you will need to follow tutorial step 1 to add a secret key - secrets aren't copied to the new Replit) - Register for an OpenWeather API key, if you haven't already (step 1 in Configure OpenWeather API key
Wrap-up
We learned so much!
- Reading/writing files
- Working with files & folders
- Argument parsing
- Error handling
- HTTP requests & APIs
- Python frameworkds
What's next?! 🎉 🐍
Learning opps
- GDI Python 2 Cohort (next session June 13-29)
- Real Python tutorials are great
- Udemy offers a wide variety of Python courses
Next topics to explore
- Custom classes (Object-oriented programming)
- Decorators/higher order functions
- Containerizing & deploying Python apps
- Testing
But really, you need to practice coding!
Hands-on project ideas: